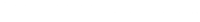The GRoLTS-Checklist: Guidelines for Reporting on Latent Trajectory Studies
Estimating models within the mixture model framework, like latent growth mixture modeling (LGMM) or latent class growth analysis (LCGA), involves making various decisions throughout the estimation process. This has led to a wide variety in how results of latent trajectory analysis are reported.
Simulation Study Introducing the BRMSEA
Evaluating model fit in Bayesian confirmatory factor analysis with large samples: Simulation study introducing the BRMSEA
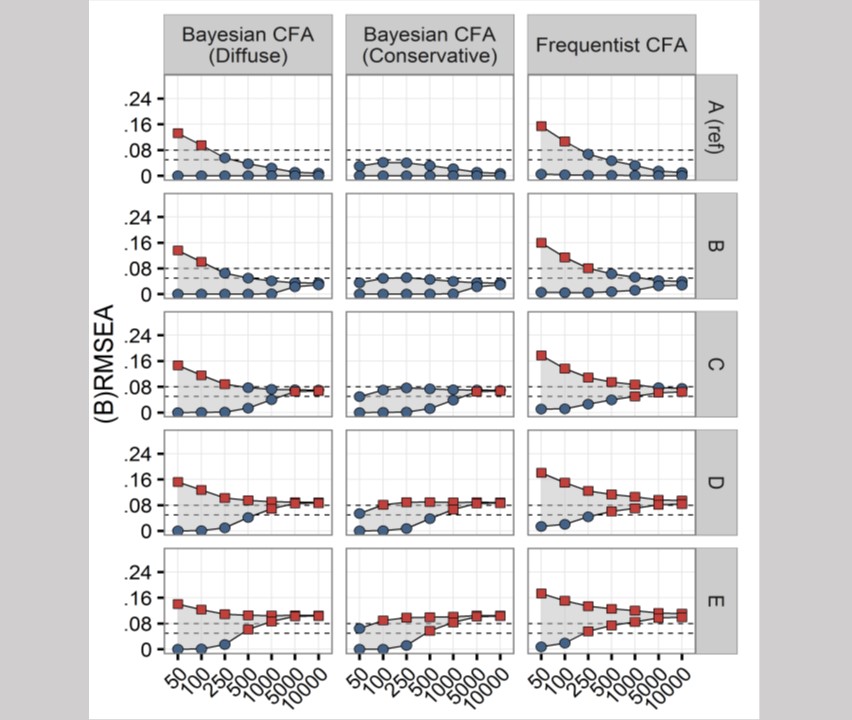
Parents’ posttraumatic stress after burns in their school-aged child: A prospective study
Objective: This prospective study examined the course and potential predictors of parents’ posttraumatic stress symptoms (PTSS) after burn injury in their child (Age 8 to 18 years). Method: One hundred eleven mothers and 91 fathers, representing 118 children, participated in the study.
Computing complexity for the Bayes Factor in inequality constrained hypotheses
The computation of complexity for the Bayes Factor is described in this tutorial.
Longitudinal Modeling
Typical for developmental psychology are models that capture change over time, such as latent growth (mixture) models and to a lesser extent cross-lagged panel models too. Such models have typically been applied aiming to capture change over time in individuals.
Small Samples
Researchers often have difficulties collecting enough data to obtain statistical power: when target groups are small (e.g., children with severe burn injuries), hard to access (e.g., infants of drug-dependent mothers), or measuring the participants requires prohibitive costs (e.g., measuring phonological difficulties of babies). Such obstacles to collecting data usually leads to a limited data set. Researchers can overcome this through simplifying their hypotheses and statistical models. However, this strategy is undesirable since the intended research question cannot be answered in this way.
Multilevel
Individuals can be conceptualized as a hierarchical system of individuals nested within groups. Such systems can be observed at different ‘levels’, and variables explaining differences between individuals and/or groups may be defined at each level. This leads to research generally referred to as ‘multilevel research’.
My First Bayes
Since the beginning of the 21st century, Bayesian statistical methods are slowly creeping into all fields of science and are becoming ever more popular in applied research.
A coach in your pocket: on chronic cancer-related fatigue and physical behavior
In this dissertation, we focused on two alternative approaches to evaluate the hypothesis of interest more directly, i.e. informative hypothesis testing and model selection using order-restricted information criteria.
Wat zijn de regels van de wetenschap en liggen die voor altijd vast?
“Lang… lang geleden, in een dorp hier ver vandaan, stelden de eerste wetenschappers Vragen. Op een dag besloten zij dat Vragen stellen veel beter ging als ze zich terugtrokken uit het dorp en in een ivoren toren gingen werken. Daar konden zij in alle rust zoeken naar mogelijke antwoorden op de Vragen.
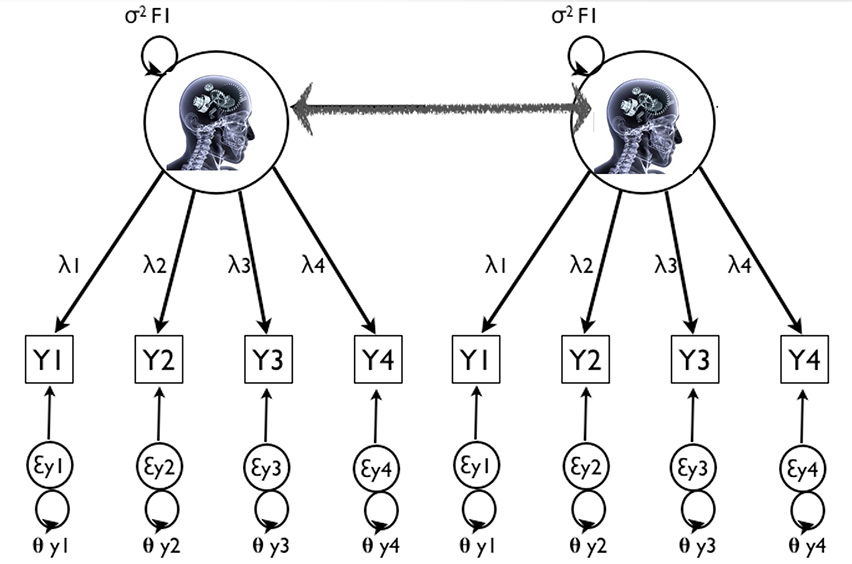
Measurement Invariance
To assess the presence of abstract concepts in people, like prolonged grief disorder, peritraumatic dissociation and students’ motivation, surveys can be used. When concepts are operationalized by means of questions or “items”, they are called “latent variables”.
Beyond Null Hypthesis Testing
Many researchers have no particular interest in a null hypothesis assuming that “nothing is going on”, so why test it at all? Evaluating specific, directional expectations produces more insightful results than sequentially testing traditional null hypotheses against catch-all rivals.