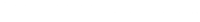Health-related quality of life after burns: A prospective multicenter cohort study with 18 months follow-up
Health-related quality of life (HRQOL) is an important parameter after medical treatments. Knowledge of (predictors of) diminished quality of life can help improve medical outcome.
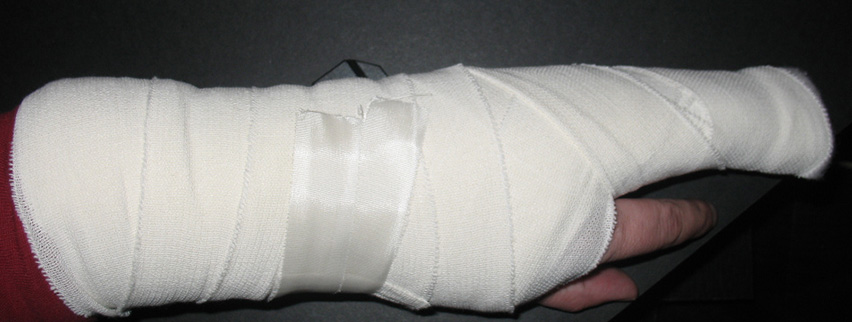
Illustrating Bayesian evaluation of informative hypotheses for regression models
In the present article we illustrate a Bayesian method of evaluating informative hypotheses for regression models. Our main aim is to make this method accessible to psychological researchers without a mathematical or Bayesian background.
Impact of pediatric burn camps on participants’ self esteem and body image: An empirical study
Quantitative as well as qualitative measures was used. To study possible effects, a pretest–posttest comparison group design with a follow-up was employed. Self-report questionnaires were used to measure self esteem and body image in a burn camp group (n = 83, 8–18 years) and in a comparison group of children with burns who did not attend a burn camp during the course of the study (n = 90, 8–18 years).
Cytokine Production by Leukocytes of Military Personnel with Depressive Symptoms after Deployment to a Combat-Zone: A Prospective, Longitudinal Study
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is frequently diagnosed in military personnel returning from deployment. Literature suggests that MDD is associated with a pro-inflammatory state. To the best of our knowledge, no prospective, longitudinal studies on the association between development of depressive symptomatology and cytokine production by peripheral blood leukocytes have been published.
An introduction to Bayesian model selection for evaluating informative hypotheses
Most researchers have specific expectations concerning their research questions. These may be derived from theory, empirical evidence, or both. Yet despite these expectations, most investigators still use null hypothesis testing to evaluate their data, that is, when analysing their data they ignore the expectations they have.
PhD monitor 2011: PhD candidates from Utrecht University speak
Het oordeel van promovendi van de Universiteit Utrecht over opleiding, begeleiding en onderzoeksfaciliteiten.
Islamic and homosexual in the Netherlands – a double mental burden?
According to the Minority Stress Model, immigrants have an increased risk of mental health problems compared with the general population. Homosexual feelings can form an additional minority stress factor next to ethnic minority status, given the social disapproval of homosexuality within non-Western cultures,
The associations of humorous coping styles, affective states, job demands and job control with the frequency of upper respiratory tract infection
There is some evidence that job demands and job resources such as job control and humorous coping may contribute to the risk of upper respiratory tract infections (URTI).
The fate of PhD projects: Efficiency of social sciences subsidies
Eenderde van het Nederlandse promotieonderzoek wordt gefinancierd vanuit NWO. Het rendement hiervan is tot nu echter niet bekend. Rens van de Schoot, Hans Sonneveld en Ditte Lockhorst onderzochten de afloop van promotieprojecten bij de gedrags- en maatschappijwetenschappen.
Directly evaluating expectations or testing the null hypothesis? Null hypothesis testing versus Bayesian model selection
Researchers in psychology have specific expectations about their theories. These are called informative hypothesis because they contain information about reality. Note that these hypotheses are not necessarily the same as the traditional null and alternative hypothesis.